pseudomembranous colitis in babies
The primary cytotoxin of C difficile toxin B may also be found in these infants but the presence of toxin A which causes intestinal fluid accumulation and mucosal necrosis in hamsters has not been demonstrated 3. Ten cases of antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis in children are reviewed.

Diy Essential Oil Blends Diy Digize Blend Diy Essential Oils Essential Oil Blends Essential Oil Blends Diy
It is most often seen in people who are in the hospital.
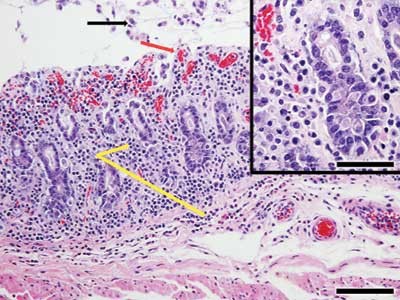
. Identification of Clostridium difficile as the major pathogen has led to a rational successful approach to therapy and has widened the spectrum of associated disease. Clostridium difficile is the most common nosocomial pathogen of the gastrointestinal tract and has increased in frequency over time. Richardson SA Brookfield DS French TA Gray J.
Pseudomembranous colitis in a 5-week-old infant. Ampicillin amoxicillin the second- and third-generation cephalosporins and clindamycin. Br Med J Clin Res Ed.
However it is becoming more common in people who take antibiotics and are not in a hospital. Treating recurring pseudomembranous colitis. Pseudomembranous colitis in children INTRODUCTION.
This review presents the microbiology management and prevention of pseudomembranous colitis PMC in children. Clostridium difficile and the aetiology of pseudomembranous colitis. With each recurrence your chance of having an additional recurrence increases.
The patients developed acute abdomen and underwent laparotomy that showed necrosis of the bowel. The most frequently implicated antimicrobial agents were penicillins in six children and clindamycin in two. Stool assays showed specimens from all ten patients yielded a cytopathic toxin which was neutralized by Clostridium sordellii antitoxin.
The ages ranged from 4 years to 17 years. Colonoscopy found that PMC occurs mainly in the colon sigmoid colon and rectum in up to 80 100 of cases. While almost any antibiotic can cause pseudomembranous colitis some antibiotics are more commonly linked to pseudomembranous colitis than others including.
Viscidi RP Bartlett JG. Ampicillin penicillin and clindamycin are the drugs most frequently reported to cause pseudomembranous colitis in pediatric patients. Pseudomembranous colitis in children.
Pseudomembranous colitis is a nonspecific pattern of injury resulting from decreased oxygenation endothelial damage and impaired blood flow to the mucosa that can be triggered by a number of disease states. Pseudomembranous colitis PMC is commonly associated with hospitalization and prior antibiotic exposure. Pseudomembranous colitis PMC occurs rarely in children but its incidences are increasing due to frequent antibiotic use.
Pseudomembranous colitis remains a potentially lethal complication of antibiotic usage. Use of medicines that weaken the immune system such as chemotherapy medicines. Pseudomembranous colitis in children and adults.
Stool assays showed specimens from all ten patients yielded a cytopathic toxin which was neutralized by. Pseudomembranous colitis PMC occurs mainly in adults and is believed to be caused almost exclusively by toxins produced by Clostridium difficile. Bolton RP Thomas DF.
The most frequently implicated antimicrobial agents were penicillins in six children and clindamycin in two. Fluoroquinolones such as ciprofloxacin Cipro and levofloxacin Penicillins such as amoxicillin and ampicillin Clindamycin Cleocin. Ten cases of antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis in children are reviewed.
Pseudomembranous colitis PMC is inflammation in your colon that happens when theres too much of certain bacteria in your system. This diagnosis should be suspected in any child with significant diarrhea during or after a course of antimicrobial therapy especially if the diarrhea persists after the drug has been discontinued. Use of medicines that weaken the immune system such as chemotherapy medicines.
It is caused almost exclusively by toxins produced by Clostridium difficile. Difficile infection include diarrhea which is usually nonbloody or colitis associated with severe abdominal pain fever andor gross or occult blood in the stools. Pseudomembranous colitis PMC the severest.
The same numbers of C difficile found in adults with pseudomembranous colitis may be present in infants with no obvious adverse effects 3. Chemicals medications ischemia microscopic colitis other infectious organisms and inflammatory conditions. It has changed in the last 100 years from a fatal disease caused by a postoperative event to in the era of antibiotics a commonly occurring complication of antibiotic use that may lead to serious morbidity but that usually is treated easily.
Typical symptoms of C. Difficile which are more resistant to antibiotics has made treating pseudomembranous colitis increasingly difficult and recurrences more common. Clostridial toxin in faeces of healthy infants.
Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis in children. PMC is commonly associated with prior antibiotic exposure and hospitalization. It is caused almost exclusively by toxins produced by Clostridium difficile.
The clinical spectrum of this disease may range from a mild non-specific diarrhea to severe colitis. Pseudomembranous colitis is an inflammatory disease of the colon see image below. It is most often seen in people who are in the hospital.
However it is becoming more common in people who take antibiotics and are not in a hospital. The bacterium that causes PMC isClostridium difficile or C. Colonoscopy is simple and fast.
The ages ranged from 4 years to 17 years. Pseudomembranous colitis is uncommon in children and rare in infants. Pseudomembranous colitis PMC occurs rarely in children but its incidences are increasing due to frequent antibiotic use.
Pseudomembranous colitis is uncommon in children and rare in infants. The natural occurrence of new more-aggressive strains of C. PMC is commonly associated with prior antibiotic exposure and hospitalization.
Rietra PJ Slaterus KW Zanen HC Meuwissen SG. This review presents the microbiology management and prevention of pseudomembranous colitis PMC in children. Two cases of ischemic necrosis of the sigmoid colon associated with pseudomembranous colitis due to Schistosoma mansoni in children have been reported.
Jayakar AV Desai AG Dalal NJ Shah SC Narayan K.

Pin By Raghav Tiwari On Medicine Inflammatory Bowel Disease Crohns Disease Pseudomembranous Colitis
Common Pain Relievers May Worsen C Difficile Infection
Frontiers How Does Covid 19 Pandemic Impact On Incidence Of Clostridioides Difficile Infection And Exacerbation Of Its Gastrointestinal Symptoms Medicine
Clostridioides Clostridium Difficile Colitis Workup Approach Considerations Stool Examination And Stool Assays Endoscopy

Choosing The Best Probiotic For C Diff Peggy Lillis Foundation

Signs And Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis Ulcerative Colitis Pseudomembranous Colitis Colitis

Diagnosis Clostridium Difficile Induced Typhlitis And Colitis Lab Animal

What Is Enterocolitis Causes Symptoms Treatment Diet

Irritable Bowel Disease Colitis Pseudomembranous Colitis

How To Diagnose And Treat Clostridium Difficile Today S Hospitalist

Day In The Life Of A Second Year Med Student While Board Studying Med Student Study Motivation Inspiration School Encouragement

Clostridium Difficile Associated Diarrhea American Family Physician
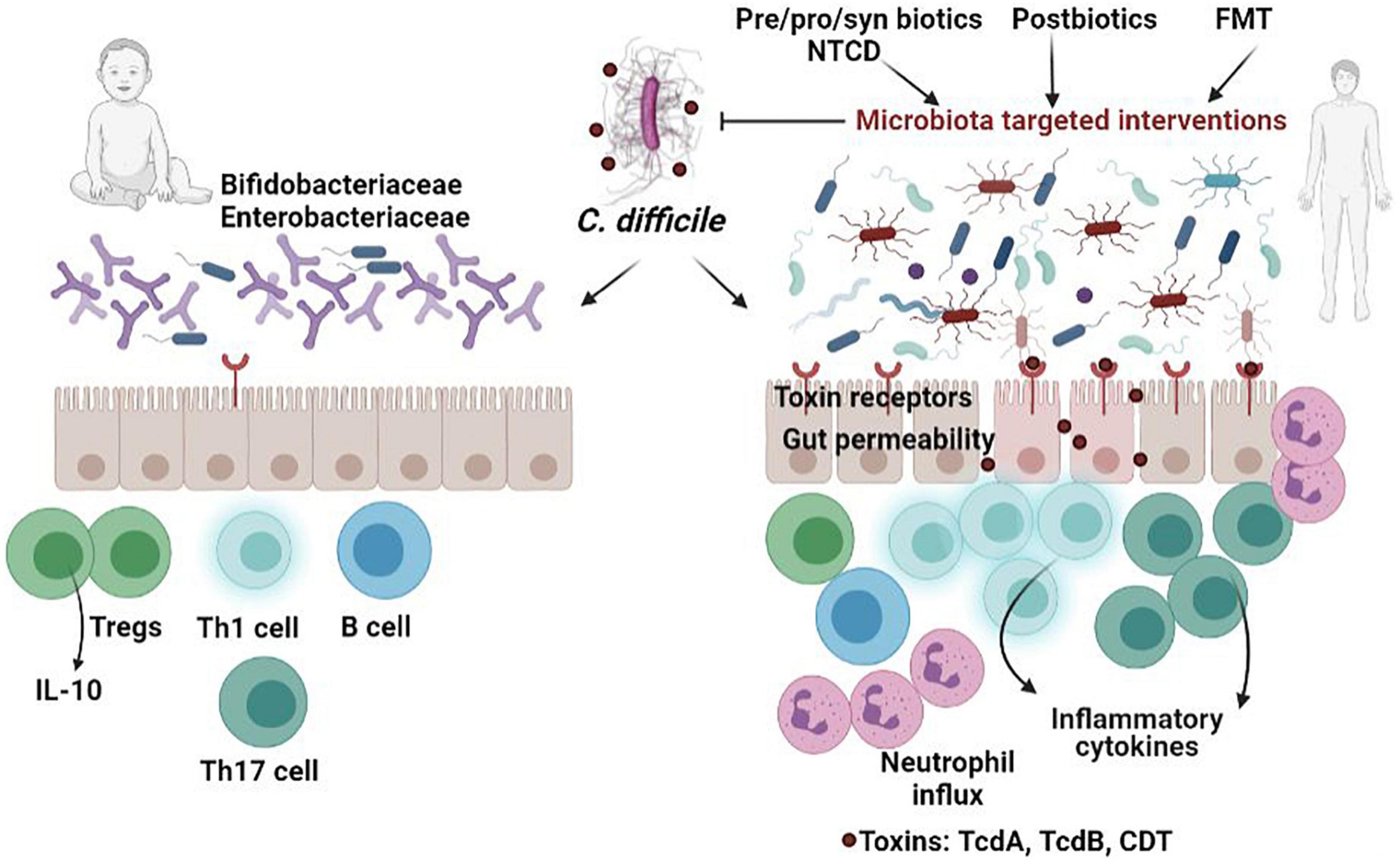
Frontiers Gut Dysbiosis And Clostridioides Difficile Infection In Neonates And Adults Microbiology

Pin On Learn Pediatrics Child Health Through Mcqs Toacs
Antibiotic Risk Factors For C Difficile Associated Diarrhea Gastrointestinal Society

Clostridium Difficile Infection What You Need To Know Consultant360

Clostridium Difficile C Diff Infectious Dis Medbullets Step 2 3

Infections Caused By C Difficile In Children Explained Wonderbaba